Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current I in a conductor and the voltage U between the ends of the conductor are directly proportional. The formula URI is a mathematical representation of this law. Ohm's law can be used to calculate the three basic quantities of an electrical circuit if at least two of them are known. The three basic quantities are voltage, current and resistance. The physicist Georg Simon Ohm established and proved the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. Ohm's law was named after him.
It is important to understand that Ohm's law only applies to ohmic resistors. This includes normal resistors and components that have a linear relationship between voltage and current. The resistance of a diode or a lamp cannot be calculated using Ohm's law, as the current and voltage on these components do not have a linear relationship. Normal resistors always have the same value within their limit values, regardless of voltage and current. Only this resistance value can be calculated using Ohm's law.
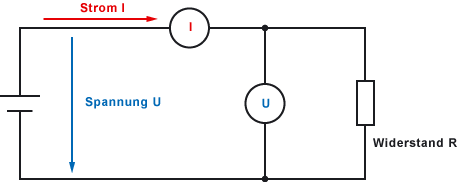
To simplify the calculation,
we have expanded the "Online calculator" section for you with the formulae listed here.
Units of measurement used:
Voltage U=Volt [V]
Current I=Ampere [A]
Resistance R=Ohm [Ω]
